함수를 활용한 여러 변수 선택
- filter( ) : 메서드에서 변수 이름 패턴을 활용한 선택 (열 선택)
display(df_pr.filter(regex='se$') )
#위의 문장과 같은 역할을 한다
df_pr.loc[:,['Exercise']]
Exercise
0 2
1 2
2 1
3 1
4 3
... ...
105 3
106 3
107 3
108 1
109 2
110 rows × 1 columnsregex : 정규표현식(regular expression), str(문자열)을 포함함
'^s' : 's'로 시작하는 이름/텍스트
's$' : 's'로 끝나는 이름/텍스트
- . dtypes: 변수형식 확인
df_ins.dtypes
age int64
sex object
bmi float64
children int64
smoker object
region object
charges float64
dtype: object int/float : 숫자
object : 문자열
변수 형식으로 선택
- include= ' 변수 형식' : '변수 형식'과 같은 변수를 선택함
- exclude= '변수 형식' : 변수 형식'과 같은 변수를 제외함
df_ins.select_dtypes(include='number')
age bmi children charges
0 19 27.900 0 16884.92400
1 18 33.770 1 1725.55230
2 28 33.000 3 4449.46200
3 33 22.705 0 21984.47061
4 32 28.880 0 3866.85520
... ... ... ... ...
1333 50 30.970 3 10600.54830
1334 18 31.920 0 2205.98080
1335 18 36.850 0 1629.83350
1336 21 25.800 0 2007.94500
1337 61 29.070 0 29141.36030
1338 rows × 4 columns수치형(int, float) 변수
df_ins.select_dtypes(include='object')
sex smoker region
0 female yes southwest
1 male no southeast
2 male no southeast
3 male no northwest
4 male no northwest
... ... ... ...
1333 male no northwest
1334 female no northeast
1335 female no southeast
1336 female no southwest
1337 female yes northwest
1338 rows × 3 columns문자형(object) 변수
조건을 활용한 관측치 선택 :SQL에서 WHERE 절이나 Excel의 Filter와 같이 데이터에서 부분을 선택할 때 조건을 활용하는 경우 많음, [ ]나. loc [ ] 안에 조건식을 넣어서 조건과 일치하는 관측치만 선택 가능
- 1 단계 : 조건 설정(결과는 True/False) (bool 타입 Series)
- 2 단계 : [ ]와 조건을 활용한 관측치 선택
- 3 단계 : &와 |를 활용한 조건 결합( and -> & , or -> | ), 같은 인덱스끼리 연산함
# 1 단계
cond1 = df_ins['age'] < 30
# 2 단계
cond2 = df_ins['sex'] == 'female'
# 3 단계
cond = cond1 & cond2
df_ins[cond]
#위의 것과 같은 결과
df_ins[(df_ins['age'] < 30) & (df_ins['sex'] == 'female')]
#나이 30 미만 중 여성 선택
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
0 19 female 27.900 0 yes southwest 16884.92400
31 18 female 26.315 0 no northeast 2198.18985
32 19 female 28.600 5 no southwest 4687.79700
40 24 female 26.600 0 no northeast 3046.06200
46 18 female 38.665 2 no northeast 3393.35635
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
1328 23 female 24.225 2 no northeast 22395.74424
1331 23 female 33.400 0 no southwest 10795.93733
1334 18 female 31.920 0 no northeast 2205.98080
1335 18 female 36.850 0 no southeast 1629.83350
1336 21 female 25.800 0 no southwest 2007.94500
201 rows × 7 columns- isin()을 활용한 특정 수준 관측치 선택
cond1 = df_ins['region'].isin(['southeast','northwest'])
# 위에 코드랑 같은 결과
(df_ins['region'] == 'southeast') | (df_ins['region'] == 'northwest')
0 False
1 True
2 True
3 True
4 True
...
1333 True
1334 False
1335 True
1336 False
1337 True
Name: region, Length: 1338, dtype: boolisin() 뒤에 있는 게 있으면 True, 없으면 False(둘 중 하나만 있어도 True)
- Series의 between 메서드 : 특정 범위 내 관측치 선택 가능
# between(a>= n, b<=n)
cond1 = df_sp['math score'].between(80, 90, inclusive='left')
0 False
1 False
2 False
3 False
4 False
...
995 True
996 False
997 False
998 False
999 False
Name: math score, Length: 1000, dtype: bool 양쪽 끝 경계 포함 여부 지정 가능( 'both', 'left', 'right', 'neither')
bool Series(True/False) 앞에 ~ 를 붙여서 True와 False를 뒤집기 가능 (EX : ~cond1)
- . query() 메서드
df_sp.query('`math score`>= 90')90점 이상을 찾음
함수를 활용한 부분 관측치 선택
- head( )와 tail()
display("head()",df_ins.head())
display("tail()",df_ins.tail())
'head()'
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
0 19 female 27.900 0 yes southwest 16884.92400
1 18 male 33.770 1 no southeast 1725.55230
2 28 male 33.000 3 no southeast 4449.46200
3 33 male 22.705 0 no northwest 21984.47061
4 32 male 28.880 0 no northwest 3866.85520
'tail()'
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
1333 50 male 30.97 3 no northwest 10600.5483
1334 18 female 31.92 0 no northeast 2205.9808
1335 18 female 36.85 0 no southeast 1629.8335
1336 21 female 25.80 0 no southwest 2007.9450
1337 61 female 29.07 0 yes northwest 29141.3603head() : 처음 n개의 행을 반환
tail() : 마지막 n개의 행을 반환
- sample( ) : 랜덤으로 추출
df_ins.sample(n=10)frac=0.005 : 비율로 추출 (EX: df_ins.sample(frac=0.005))
- nlargest( ), nsmallest( ) : 상위/하위 관측치 선택
df_ins.nlargest(10, 'charges')
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
543 54 female 47.410 0 yes southeast 63770.42801
1300 45 male 30.360 0 yes southeast 62592.87309
1230 52 male 34.485 3 yes northwest 60021.39897
577 31 female 38.095 1 yes northeast 58571.07448
819 33 female 35.530 0 yes northwest 55135.40209
1146 60 male 32.800 0 yes southwest 52590.82939
34 28 male 36.400 1 yes southwest 51194.55914
1241 64 male 36.960 2 yes southeast 49577.66240
1062 59 male 41.140 1 yes southeast 48970.24760
488 44 female 38.060 0 yes southeast 48885.13561
df_ins.nsmallest(10, 'charges')
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
940 18 male 23.21 0 no southeast 1121.8739
808 18 male 30.14 0 no southeast 1131.5066
1244 18 male 33.33 0 no southeast 1135.9407
663 18 male 33.66 0 no southeast 1136.3994
22 18 male 34.10 0 no southeast 1137.0110
194 18 male 34.43 0 no southeast 1137.4697
866 18 male 37.29 0 no southeast 1141.4451
781 18 male 41.14 0 no southeast 1146.7966
442 18 male 43.01 0 no southeast 1149.3959
1317 18 male 53.13 0 no southeast 1163.4627nlargest(개수, 기준), nsmallest(개수, 기준)
중복값 제거
- drop_duplicates() : 중복값을 제거한 목록 생성 가능
df_ins.drop_duplicates(subset=['sex', 'region'])
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
0 19 female 27.900 0 yes southwest 16884.92400
1 18 male 33.770 1 no southeast 1725.55230
2 28 male 33.000 3 no southeast 4449.46200
3 33 male 22.705 0 no northwest 21984.47061
4 32 male 28.880 0 no northwest 3866.85520
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
1333 50 male 30.970 3 no northwest 10600.54830
1334 18 female 31.920 0 no northeast 2205.98080
1335 18 female 36.850 0 no southeast 1629.83350
1336 21 female 25.800 0 no southwest 2007.94500
1337 61 female 29.070 0 yes northwest 29141.36030
1337 rows × 7 columnssubset을 기준으로 중복된 것을 없앰
관측치 정렬
- sort_values() : 관측치를 정렬
df_ins.sort_values(['age', 'charges'], ascending=[True, False])
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
803 18 female 42.240 0 yes southeast 38792.68560
759 18 male 38.170 0 yes southeast 36307.79830
161 18 female 36.850 0 yes southeast 36149.48350
623 18 male 33.535 0 yes northeast 34617.84065
57 18 male 31.680 2 yes southeast 34303.16720
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
768 64 female 39.700 0 no southwest 14319.03100
801 64 female 35.970 0 no southeast 14313.84630
752 64 male 37.905 0 no northwest 14210.53595
534 64 male 40.480 0 no southeast 13831.11520
335 64 male 34.500 0 no southwest 13822.80300
1338 rows × 7 columns
기본은 오름차순, age는 오름차순(ascending=True), charges는 내림차순(asending=False)
- index를 활용한 정렬
df_ins = df_ins.sort_index()
df_ins
age sex bmi children smoker region charges
0 19 female 27.900 0 yes southwest 16884.92400
1 18 male 33.770 1 no southeast 1725.55230
2 28 male 33.000 3 no southeast 4449.46200
3 33 male 22.705 0 no northwest 21984.47061
4 32 male 28.880 0 no northwest 3866.85520
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
1333 50 male 30.970 3 no northwest 10600.54830
1334 18 female 31.920 0 no northeast 2205.98080
1335 18 female 36.850 0 no southeast 1629.83350
1336 21 female 25.800 0 no southwest 2007.94500
1337 61 female 29.070 0 yes northwest 29141.36030
1338 rows × 7 columns
데이터 집계와 데이터 처리
수치형 변수의 집계값과 히스토그램 : 하나의 수치형 변수로 합계, 평균과 같은 집계값을 계산할 수 있고 히스토그램으로 분포를 확인
- 수치형 변수의 집계값 계산
df_ins['charges'].mean()
13270.422265141257
df_ins['charges'].sum()
17755824.990759
df_ins['charges'].var(), df_ins['charges'].std()
(146652372.1528548, 12110.011236693994)
df_ins['charges'].median()
9382.033
df_ins['region'].count()
1338mean( ) : 평균
sum() : 합계
var() , std() : 분산과 표준편차
median() : 중앙값
count() : 관측치 수
- 히스토그램 그리기
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns라이브러리 불러오기
df_ins['age'].plot(kind='hist')
plt.show()
DataFrame의 plot 메서드 활용
plt.show() : 최종 그래프 출력함수, 생략 가능
sns.histplot(data=df_ins, x='age')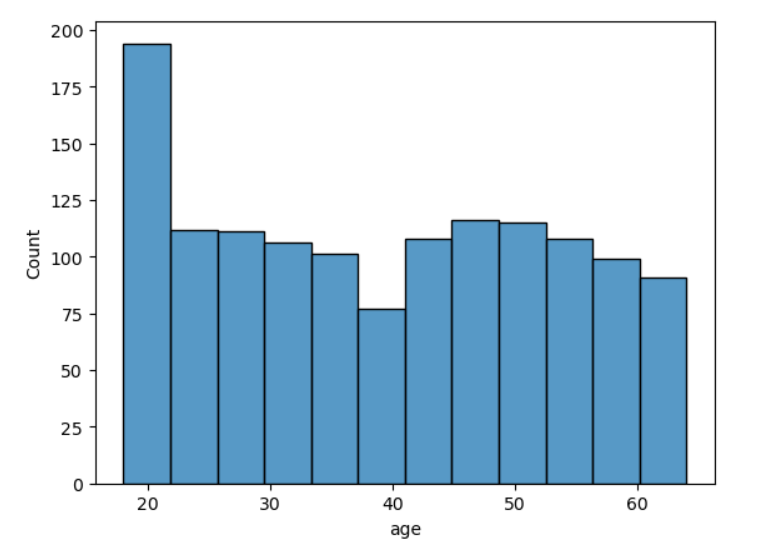
- 분위수 : 최솟값(minimum, 0%), Q1(1st Quartile, 25%), 중앙값(median, 50%), Q3(3rd Quartile, 75%), 최댓값(maximum, 100%)을 사분위수(quartile)이라고 부름
df_ins['charges'].quantile([0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0])
0.00 1121.873900
0.25 4740.287150
0.50 9382.033000
0.75 16639.912515
1.00 63770.428010
Name: charges, dtype: float64quantile( ) : 계산할 분위(1.0이 최댓값)를 리스트로 묶기
- 상자그림(boxplot)
import seaborn as sns
# df_sp에서 'reading score'의 Q1(25%), 중위수(median, 50%), Q3(75%) 계산하기
print(df_sp['reading score'].quantile([0.25,0.5,0.75]))
# df_sp에서 'reading score'의 상자그림을 seaborn으로 그리기
display(" 'reading score'의 상자그림",sns.boxplot(data = df_sp,y = 'reading score'))
0.25 59.0
0.50 70.0
0.75 79.0
Name: reading score, dtype: float64
범주형 변수의 요약과 시각화
범주형 변수는 정해진 수준(level) 중에 하나의 값을 갖기 때문에 분석 방법이 단순하며 개수를 세면 됨
- 그룹별 건수 계산과 시각화 : 범주형 변수/그룹 변수로 수준별 관측치 수를 셀 수 있다.
df_ins['smoker'].value_counts()
smoker
no 1064
yes 274
Name: count, dtype: int64value_counts() : 수준별 관측치 수 세기
sns.countplot(data=df_ins, x='smoker')
산점도와 상관계수의 활용
두 수치형 변수의 관계를 파악
- seaborn으로 산점도 그리기
mean_f = df_heights['father'].mean()
mean_s = df_heights['son'].mean()
print(mean_f, mean_s)
# plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plot_scatter = sns.scatterplot(data=df_heights, x='father', y='son', alpha=0.3)
# plot_scatter.axhline(mean_s) # 수평선 추가
# plot_scatter.axvline(mean_f) # 수직선 추가
df_heights[['father','son']].cov()
father son
father 48.608307 24.989192
son 24.989192 51.113092
df_heights[['father','son']].corr()
father son
father 1.000000 0.501338
son 0.501338 1.000000공분산, 상관관계 계산 : 상관관계가 커질수록 연관성이 큼
그룹별 집계값의 계산과 분포 비교
범주형 변수를 그룹처럼 활용해서 그룹별 평균을 계산하고, 그룹별 상자그림을 그려서 그룹 간 분포를 비교
한 변수의 집계에서 groupby()를 추가하면 되고, 필요에 따라 agg()를 활용 가능
1. 그룹을 나눔
2. 변수 선택
3. 집계 선택
- 그룹별 평균 계산(DataFrame 형식으로 출력)
df_ins.groupby(['sex','smoker'], as_index=False)['charges'].agg(['min','max','mean'])
sex smoker min max mean
0 female no 1607.5101 36910.60803 8762.297300
1 female yes 13844.5060 63770.42801 30678.996276
2 male no 1121.8739 32108.66282 8087.204731
3 male yes 12829.4551 62592.87309 33042.005975groupby() : 그룹별 평균 계산(여러 개의 그룹 변수 가능)
as_index= : 데이터 프레임으로 변경, (기본은 True(시리즈로 출력))
agg() : 여러 집계값 계산
[실습] 변수 관계 탐색
1. 데이터 df_sp에서 범주형 변수(열) 하나를 선택해서 그룹을 나눈 후 수치형 변수(열) 하나를 선택하여 평균을 계산 및 상자그림 그리기
2. 데이터 df_sp에서 임의의 두 범주형 변수(열)를 선택하여 math score의 평균을 계산하기
3. 의 세 변수를 x, y, hue로 활용해 seaborn으로 상자그림 그리기
# 1. 데이터 df_sp에서 범주형 변수(열) 하나를 선택해서 그룹을 나눈 후 수치형 변수(열) 하나를 선택하여 평균을 계산 및 상자그림 그리기
# 범주형 gender, 수치형 math score
display(df_sp.groupby('gender', as_index=False)['math score'].mean())
sns.boxplot(data = df_sp, x ='gender',y ='math score')
gender math score
0 female 63.633205
1 male 68.728216
# 2. 데이터 df_sp에서 임의의 두 범주형 변수(열)를 선택하여 math score의 평균을 계산하기
df_sp.groupby(['gender','race/ethnicity'],as_index=False)['math score'].mean()
gender race/ethnicity math score
0 female group A 58.527778
1 female group B 61.403846
2 female group C 62.033333
3 female group D 65.248062
4 female group E 70.811594
5 male group A 63.735849
6 male group B 65.930233
7 male group C 67.611511
8 male group D 69.413534
9 male group E 76.746479# 3.의 세 변수를 x, y, hue로 활용해 seaborn으로 상자그림 그리기
sns.boxplot(data = df_sp , x= 'race/ethnicity',y='math score',hue='gender')
'ABC 부트캠프 데이터 탐험가 4기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [10 일차] ABC 부트캠프 : 데이터 전처리 예제 (0) | 2024.07.17 |
|---|---|
| [9 일차] ABC 부트캠프 : 데이터 집계와 시각화(1) (0) | 2024.07.16 |
| [7일차] ABC 부트캠프 : pandas 기초 , 데이터 전처리 기초(1) (0) | 2024.07.14 |
| [6일차] ABC 부트캠프 : Jupyter Notebook 활용 및 Python 기초 (4) (0) | 2024.07.12 |
| [5일차] ABC 부트캠프 : Jupyter Notebook 활용 및 Python 기초 (3) (0) | 2024.07.11 |